35% of organizations have more than 50% of their workloads in the cloud, with 29% stating that they anticipate moving this number up to 75% of workloads in the cloud in the next 12-18 months. While organizations are embracing cloud infrastructure, they must also consider its pitfalls.
About 45% of breaches are cloud-based, and the average cost of a data breach is approximately USD 4.45 million. A data breach not only costs an organization a fortune but it also brings with it a loss of reputation, trust, and data. Thus, it becomes imperative for organizations relying heavily on cloud-based services to educate themselves about common cloud risks, challenges, and threats.
Most organizations use risks, threats, and challenges interchangeably. However, it is crucial to understand the nuances and differences between them to address them and secure your organization’s cloud assets effectively. Here is what each term means within the context of cloud security:
- A risk refers to a weak spot or exposure to critical data loss.
- A threat refers to an attack or damage caused to an organization.
- A challenge refers to the hurdles an organization may face when implementing cloud security measures.
This blog will delve into the top cloud security threats, risks, and challenges. Once we have listed them, we will explore the best practices and strategies for mitigating them.
Top Cloud Security Threats
80% of companies have experienced at least one cloud security incident last year. Let us uncover a few cloud security threats organizations may face in the future to understand how to mitigate their impact.
Zero-Day Attacks
A zero-day attack target recently identified vulnerabilities the organization has not yet patched. Due to the interconnected nature of cloud services, these attacks can be particularly damaging in the cloud environment. Once an attacker finds a zero-day vulnerability, they can access an organization’s cloud infrastructure, vast amounts of sensitive data, and critical systems, leading to colossal data loss or leakage.
Insider Threats
Insider threats are cyber threats that emerge from within the organization. They are usually former or current employees who may have access to sensitive data or critical cloud assets and misuse them for malicious reasons.
These individuals may also have access to networks, systems, and business processes that aid them in carrying out the attack. Managing insider threats within the cloud is challenging due to the extensive access privileges required for various services. Implementing strict access controls, continuous monitoring, and promoting a culture of security awareness can help reduce the risk posed by insiders.
Advanced Persistent Attacks
Advanced Persistent Attacks (APTs) are long-term targeted attacks in which an intruder gains access to a network and remains undetected for an extended period. They can be particularly stealthy and pose a severe threat to cloud security as they move from workload to workload, stealing sensitive information that they sell to the highest bidder.
These attacks can start as zero-day attacks but quickly transform into ATPs if they remain undetected. A few practices to overcome APTs include comprehensive security monitoring, anomaly detection systems, and regular security audits to identify and respond to suspicious activities.
Data Breaches
As mentioned above, data breaches involve unauthorized access to sensitive information, often causing irreparable damage to the organization’s finances and reputation. These breaches can occur in the cloud due to misconfigured security settings, weak access controls, or vulnerabilities in the cloud infrastructure.
Protection against security threats in cloud computing can help avoid data breaches. A multi-layered approach, including encryption, strong access management, and compliance, is required to safeguard sensitive cloud assets.
Top Cloud Security Risks
Here are some of the common cloud security risks organizations can prevent or avoid:
Unauthorized Access
A typical cloud security risk is unauthorized users accessing sensitive cloud resources without proper permissions. This can lead to data theft, service disruption, and other malicious activities. Common causes include weak passwords, lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA), and poor access management.
Organizations can mitigate unauthorized access risks by implementing strong access management mechanisms, reviewing outdated or over-privileged access, and enforcing the principle of least privilege (PoLP) to ensure users have limited access to perform their functions.
Cloud Misconfiguration
A recent survey cited cloud misconfiguration as the primary reason for security breaches in cloud environments. This security risk arises when cloud resources are not configured correctly, exposing them to attackers. Misconfigurations can occur in storage settings, network security groups, or identity and access management (IAM) policies.
Organizations should use automated tools to continuously monitor and assess cloud configurations, enforce best practices, and provide adequate training for cloud administrators to reduce this risk.
Human Error
About 68% of breaches involved a non-malicious human element, such as a person falling victim to a social engineering attack or making an error. Human error remains a significant cloud security risk for most organizations. Mistakes such as incorrectly setting up security controls, mishandling sensitive data, or falling for phishing attacks can have severe individual and organizational consequences.
Organizations can mitigate this risk by investing in comprehensive employee training programs, promoting a security-first culture, and swiftly implementing procedures to detect and rectify these errors.
Unmanaged Attack Surface
Attack surface refers to all the possible points an unauthorized user can use to enter the organization. Due to the dynamic nature of cloud resources and services, the attack surface in a cloud environment can expand rapidly. If a cloud environment’s attack surface is poorly managed or remains unmanaged, it can increase the likelihood of attackers exploiting cloud security vulnerabilities.
To address this risk, organizations should conduct regular vulnerability assessments, employ continuous monitoring solutions, and ensure proper asset management to secure their most critical cloud resources.
How to Effectively Mitigate Cloud Security Threats?
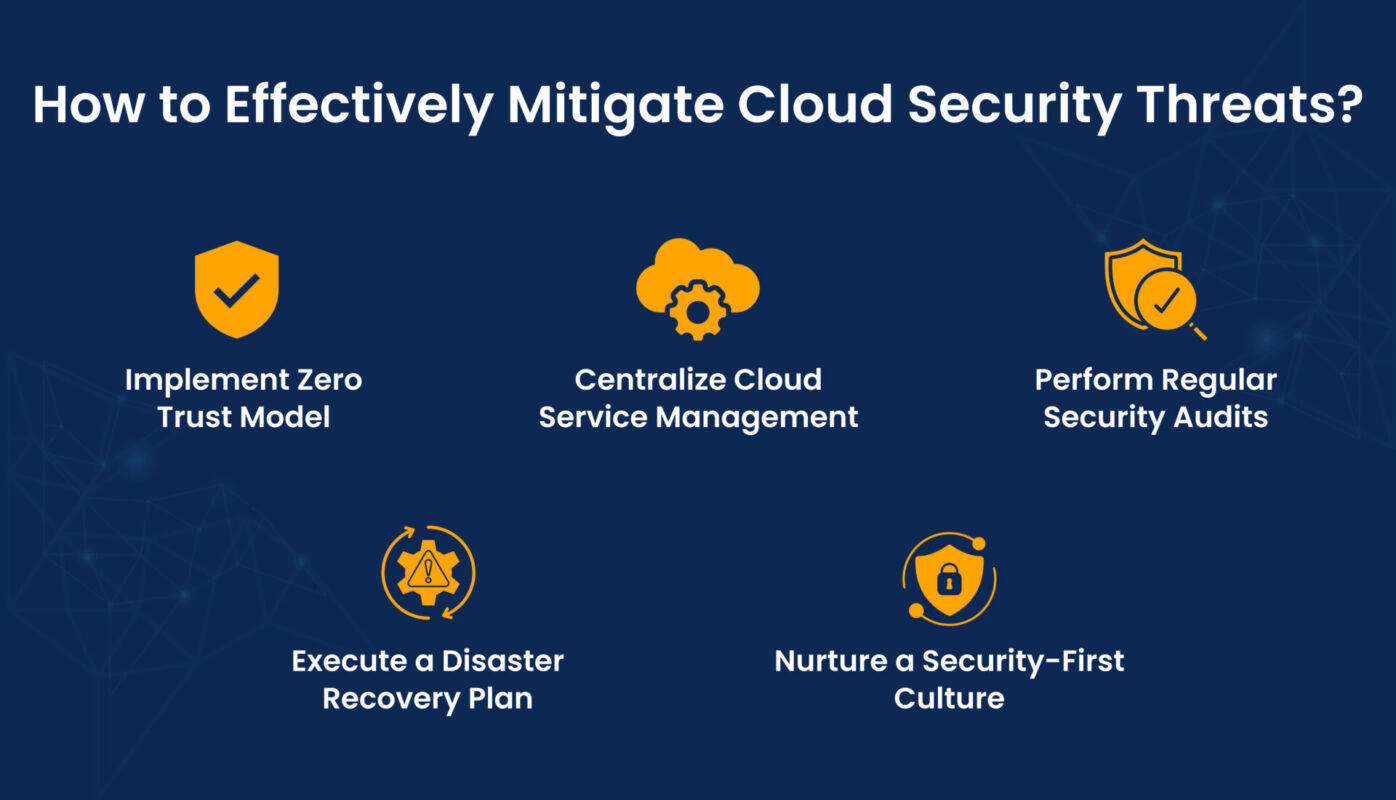
Organizations can effectively address and mitigate cloud security threats and risks by implementing security measures to secure cloud assets. Here are a few measures that help organizations actively address cloud security flaws:
Implement Zero Trust Model
Organizations can implement the Zero-Trust model when addressing cloud security concerns such as data breaches, human error, or insider threats. This model operates on the “never trust, always verify” principle and ensures that every access request is thoroughly authenticated, authorized, and encrypted.
With this approach, organizations can minimize the risk of unauthorized access by continuously validating the identity and integrity of users and devices. They can also implement practices such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), the principle of least privilege, and role-based access controls (RBAC) to enforce strict access controls and monitor user activities.
Centralize Cloud Service Management
Organizations can employ cloud security companies to centralize the management of cloud services and streamline security policies and controls across the cloud infrastructure. Cloud security companies such as Tenable Cloud Security unify siloed tools to protect different workloads across multi-cloud environments.
It provides a comprehensive view of organizations’ security posture, automates compliance checks, and allows them to deploy unified cloud-native application protection platform (CNAPP) solutions that integrate multiple cloud capabilities such as cloud infrastructure entitlement management (CIEM), cloud workload protection platform (CWPP), and cloud detection and response (CDR).
Perform Regular Security Audits
Organizations can conduct regular security audits to identify security challenges in cloud computing, such as emerging vulnerabilities, complexity of cloud environments, and compliance with cloud security policies. A thorough security audit involves a detailed examination of cloud infrastructure, configurations, and access controls to detect weaknesses or deviations from best cloud security practices.
Conducting audits regularly helps organizations stay proactive in addressing security gaps and maintaining an effective security posture. They can also utilize third-party security assessments to gain an unbiased view of their cloud environment’s security measures.
Execute a Disaster Recovery Plan
A comprehensive disaster recovery plan is vital for minimizing the impact of a cyberattack or a data breach and ensuring business continuity. Organizations must draft a plan that includes data backup, recovery, and restoration procedures in case of a security breach. They can also regularly evaluate its impact by testing and refining the disaster recovery plan. This ensures effectiveness and prepares the organization to respond swiftly to any incident.
Nurture a Security-First Culture
A cloud security strategy is incomplete if employees lack security awareness. Organizations must educate employees about the importance of security, provide regular training on security best practices, and encourage a proactive approach to identifying and reporting security threats. Moreover, they must inculcate a culture of security awareness to ensure that all employees actively understand their role in securing the organization’s cloud assets.
While these best practices may help organizations mitigate cloud security risks, organizations must consider deploying a cloud security service to address cloud security threats proactively. These services help security teams monitor attack surfaces, automate patch management and access controls, ensure compliance, identify threats, and more.
Mitigate Cloud Security Risks and Threats with ComplyTec!
ComplyTec is your organization’s trusted partner for cloud security management! We partner with your security team to develop cybersecurity solutions that strengthen protection against threats and vulnerabilities based on your organizational needs.
ComplyTec has provided IT solutions to various North American organizations, including Blue-chip companies and government agencies. We bring vulnerability management, cloud security, and identity security expertise to your organization while enhancing its operational efficiency.
Mitigate cloud security risks and secure your cloud infrastructure today!
FAQs
- What are common cloud security challenges?
A recent report finds that the top cloud challenges for all organizations are as follows :
- Security
- Lack of resources or expertise
- Managing cloud spend
- Cloud governance
- Managing software licenses
- Maintaining Compliance
- Cloud migration
- Managing multi-cloud environments
- What is cloud security threat detection and why is it important?
Cloud security threat detection involves identifying and responding to potential security threats within a cloud environment. It is crucial for the following reasons:
- Proactive Defense: Threat detection allows organizations to identify and mitigate potential security incidents before they cause significant damage.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of cloud resources helps detect unusual activities and potential threats in real-time.
- Incident Response: Effective threat detection provides information for swift incident response and remediation efforts.
- Data Protection: By identifying threats early, organizations can protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Reducing Downtime: Early detection of threats helps minimize downtime and ensure the continuity of business operations.
Additionally, implementing comprehensive threat detection solutions, such as security information and event management (SIEM) tools and machine learning-based anomaly detection, can significantly enhance an organization’s cloud security posture.
Sources:
- Proof Point
- Fingent
- Power Consulting
- Strongdm
- Exabeam
- Educative
- Netwrix
- Sify
- Indusface
- Crowdstrike