According to McKinsey’s research on the ROI of cloud adoption, almost all of the eighty enterprises it spoke to aspire to run most of their applications in the public cloud within five to seven years; more than two-thirds aspire to run 80% of their systems in the cloud. Moreover, an average company adopting the cloud today could achieve 180% ROI in business benefits.
With such a positive ROI, only 10% of companies have fully captured the cloud’s potential value, while another 50% are beginning to capture it, and the remaining 40% have seen no material value.
What could be holding organizations back from truly embracing the cloud’s potential?
81% of organizations have cited security as one of the top challenges when migrating to the cloud, followed by a lack of expertise. These statistics highlight that cloud security concerns may hinder organizations from utilizing and benefiting from the cloud’s potential.
This blog will explore how your organization can build a rigorous cloud security strategy to maximize its cloud environments. Let’s begin by understanding what a cloud security strategy is, why it is essential, and the critical elements of a cloud security strategy.
What Is a Cloud Security Strategy?
A cloud security strategy is an extensive framework that dictates how an organization must effectively protect its cloud applications, infrastructure, and ecosystem, which contain critical cloud-based assets. A multi-cloud security strategy utilizes a variety of practices, tools, and policies to secure an organization’s cloud environments.
Securing an organization’s cloud infrastructure requires it to proactively manage potential threats and vulnerabilities, which includes addressing the probability of an attack and gauging the impact of a cyberattack rather than immediately eliminating it. This makes cloud security a continuous endeavor instead of a one-time solution. Let us explore the core elements of a strong cloud security strategy.
The Core Elements of Cloud Security Strategy
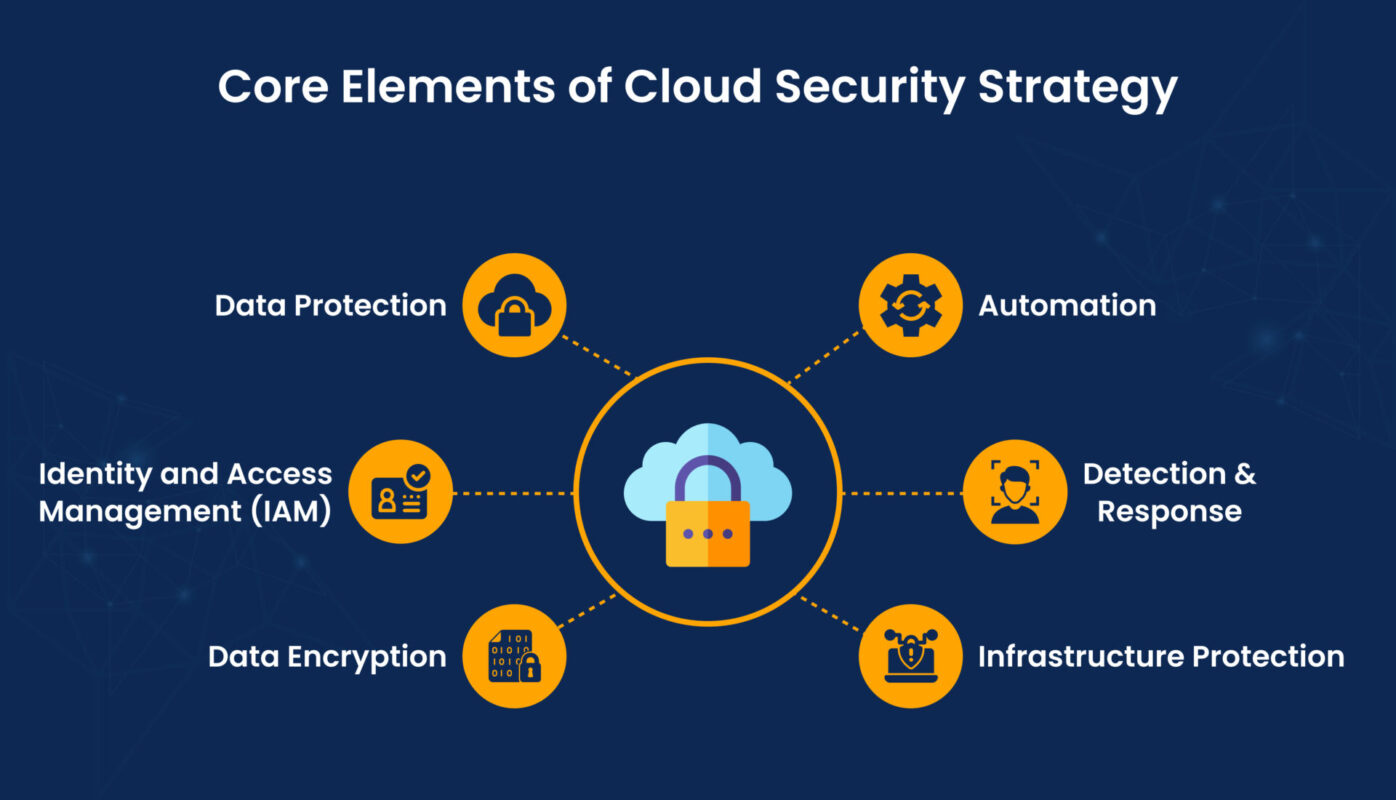
The core elements of a cloud security strategy address the unique challenges of cloud security and ensure comprehensive protection. These core elements include:
Data Protection
Data protection is fundamental to securing the cloud. It aims to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches and ensure its availability, integrity, and confidentiality. Some practices include data classification and masking to prioritize protection measures and conceal sensitive data. In addition, strong backup and disaster recovery plans ensure data integrity and availability in case of a data breach.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM is critical to cloud security as it manages user access throughout its lifecycle and continuously audits user activities and access patterns to detect anomalies and unauthorized access. IAM also applies the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) and Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) to enforce policies that govern user access based on roles and responsibilities. It also ensures that employees and users can access limited resources to perform their functions. Additionally, it implements multi-factor authentication (MFA) to verify user identities.
Data Encryption
Encryption is essential for protecting data in transit and at rest within the cloud environment. A few encryption best practices include:
- Secure communication protocols like SSL/TLS encrypt data as it moves between systems.
- Encrypting stored data using encryption algorithms to prevent unauthorized access.
- End-to-end encryption to ensure data remains encrypted throughout its lifecycle, from creation to storage and transmission.
Automation
Automation enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of cloud security by reducing manual intervention and human errors. Here are a few scenarios where automation may seem to expedite and streamline security measures, including:
- Security Configuration Management: Automating the configuration and management of security settings across cloud environments.
- Patch Management: Automatically applying patches and updates to systems and applications to address vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Monitoring: Using automated tools to continuously monitor and enforce compliance with security policies and regulatory requirements.
- Incident Response Automation: Implementing automated workflows to rapidly detect, respond to, and mitigate security incidents.
Detection & Response
Detecting and responding to security incidents promptly is crucial for minimizing damage and recovery time. A cloud security solution will use advanced analytics, machine learning, and threat intelligence to identify potential threats and anomalies. It will also implement security information and event management(SIEM)solutions to collect, analyze, and correlate security event data in real time. Moreover, it will prepare an effective incident response plan to ensure swift and coordinated actions in case of a data breach.
Infrastructure Protection
Protecting the underlying cloud infrastructure is vital for maintaining the overall security of cloud environments. Organizations can implement firewalls, intrusion detection or prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and virtual private networks (VPNs) to secure network traffic. Cloud security measures include deploying endpoint protection solutions to safeguard devices accessing cloud resources. Additionally, they protect the physical data centers where cloud infrastructure is housed through access controls, surveillance, and environmental controls.
By integrating these core elements, organizations can develop a successful cloud security strategy that mitigates risks and protects their cloud-based assets.
Challenges in Building a Cloud Security Strategy
Organizations face many challenges when creating an effective cloud security strategy. Here are a few of them and how they can address these challenges:
Complexity of Multi-Cloud Environments
As organizations increasingly adopt multi-cloud strategies, managing security measures across different cloud infrastructures and platforms becomes more complex. Each cloud provider offers unique security features and configurations, which can lead to inconsistent security policies and fragmented security management.
Organizations must ensure their security teams thoroughly understand each platform’s capabilities, features, and security practices when creating a multi-cloud security strategy to unify these measures across multiple cloud environments.
Evolution of Threats
93% of organizations had two or more identity-related breaches in the past year. The rapid evolution and sophistication of cyber threats pose a significant challenge to cloud security. Organizations find it difficult to keep up with attackers developing new techniques to exploit vulnerabilities.
The sophisticated nature of threats requires continuous monitoring and the adoption of advanced security technologies to detect and mitigate emerging threats effectively. Organizations can deploy advanced cloud security services that use threat intelligence to help them detect emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Shared Responsibility Model
With organizations adopting cloud solutions services, securing the cloud becomes a shared responsibility between the service provider and customers. While cloud providers secure the underlying infrastructure, customers must ensure the security of data, applications, and configurations.
Implementing a shared responsibility model can be challenging, as it requires a clear delineation of roles and comprehensive security measures at the customer level. However, organizations can overcome this by promoting a security-first approach across teams and integrating security into their DevOps pipeline.
Data Privacy and Compliance
Ensuring data privacy and regulatory compliance in the cloud can be complex due to varying data protection laws across regions and industries. Organizations must navigate these regulations and implement appropriate controls to protect sensitive information. This often involves encrypting data, managing access controls, and conducting regular audits to demonstrate compliance with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Effective Access Management
Managing access and privileges is crucial for securing cloud environments. However, with multiple environments and teams, gaining visibility into who has access to which assets and managing user privileges can take time and effort. Organizations must implement cloud infrastructure entitlement management (CIEM) to ensure that only authorized users can access critical and sensitive cloud assets.
Automated Security Processes
While automation can enhance cloud security, implementing and managing automated security processes can be challenging. Organizations must develop and maintain automated workflows for configuration management, patching, and incident response tasks.
They must ensure these processes are secure, reliable, and adaptable to changing security needs, which require significant expertise and resources. Organizations can also deploy cloud security solutions to help them manage automated workflows effectively and ensure unknown applications or systems do not gain access to sensitive information.
Detection and Response
Responding to security incidents within cloud environments is complex due to the volume of data and the distributed nature of cloud infrastructure. Organizations must implement advanced threat detection tools like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and develop powerful incident response plans. They must coordinate response efforts across different cloud platforms and ensure timely incident remediation.
Integration with Existing Security Tools
Integrating cloud security with existing on-premises security tools and processes can be challenging. Organizations often use a variety of security solutions that may not be fully compatible with cloud environments. Ensuring seamless integration and consistent security policies across both on-premises and cloud infrastructure requires careful planning and often necessitates additional investments in new tools and technologies.
Skills and Expertise
Building and maintaining a security strategy for the cloud requires specialized skills and expertise. The shortage of qualified cybersecurity professionals can make it difficult for organizations to find and retain the necessary talent. Organizations can overcome this challenge by investing in ongoing training and development for existing staff.
Cost Management
A report revealed that 50% of organizations cite the costs of managing cloud infrastructure as one of the challenges when migrating to the cloud. Implementing comprehensive cloud security measures can be costly, especially for organizations with limited budgets. Balancing the need for security with cost considerations requires careful planning and prioritization. Organizations must evaluate the costs and benefits of different security solutions and make strategic investments to maximize their security posture within budget constraints.
While these challenges seem complex, organizations can tackle them through strategic planning, investment in technology and talent, and continuous improvement of security practices.
Five Phases of Cloud Security
Here are the five phases of cloud security that organizations must be aware of when creating and implementing a cloud security strategy:
Gaining Visibility into Cloud Environment
The first phase of cloud security is gaining comprehensive visibility into your cloud environment. This involves understanding all aspects of your cloud infrastructure, from resources and configurations to data flows and user activities.
Achieving this visibility requires deploying advanced monitoring tools that provide real-time insights into the cloud ecosystem. These tools help organizations map their cloud assets, track usage patterns, and detect anomalies that could indicate potential security threats.
Remediating Critical Cloud Risks
Once organizations have visibility into their cloud ecosystem, the next phase focuses on identifying and remediating critical risks. This involves conducting thorough risk assessments to detect vulnerabilities and threats within the cloud infrastructure.
Security teams use various tools and techniques to scan for misconfigurations, weak access controls, and other potential security gaps. They initiate immediate remediation efforts to address these vulnerabilities and reduce the attack surface. These include applying security patches, updating configurations, or enhancing access controls to prevent exploitation.
Adopting Best Security Practices
Continuous improvement is the cornerstone of an effective security strategy, and the third phase involves adopting best practices to enhance the overall security posture. Organizations must stay ahead of the latest security trends, frameworks, and guidelines to implement adequate security measures. These measures include regular security audits, compliance checks, and the adoption of standard practices such as zero-trust architecture, the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP), and data encryption.
Integrating Security in DevSecOps Pipeline
Security is usually an afterthought when it comes to software development. The fourth phase emphasizes integrating security early in the software development lifecycle to prevent security flaws within software and applications. This approach involves automated security testing and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
Implementing Detection and Response
The final phase of cloud security focuses on implementing detection and response capabilities. Despite best efforts to prevent security incidents, organizations may find themselves dealing with the aftermath of an attack.
It is crucial to have advanced detection systems in place to identify suspicious activities and potential breaches in real time. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and advanced threat intelligence play a vital role in detecting anomalies and triggering alerts.
Once a potential threat is detected, having a well-defined incident response plan enables organizations to respond swiftly and effectively to contain and mitigate the impact. Regular drills and simulations ensure the response teams are well-prepared to handle an actual data breach, minimizing damage and ensuring quick recovery.
With this holistic approach, organizations can protect their cloud environments against current threats and be resilient against future challenges.
Safeguard Your Cloud Ecosystem with ComplyTec!

ComplyTec is your organization’s trusted partner for cloud security management! We partner with your security team to develop cybersecurity solutions that strengthen protection against threats and vulnerabilities based on your organizational needs.
ComplyTec has provided IT solutions to various North American organizations, including Blue-chip companies and government agencies. We bring vulnerability management, cloud security, and identity security expertise to your organization while enhancing its operational efficiency.
Safeguard your cloud environments today with ComplyTec!
Contact Us
FAQs
- How to build a successful cloud security strategy?
Here is how your organization or security team can build a successful cloud security strategy:
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Identify and evaluate potential threats and vulnerabilities specific to your cloud environment.
- Implement Access Controls: Restrict access to sensitive data and applications by using strong authentication methods and defining user roles.
- Ensure Data Protection: Encrypt data in transit and at rest to safeguard it from unauthorized access.
- Maintain Compliance: Adhere to relevant regulatory requirements and industry standards to ensure legal and ethical data handling.
- Develop an Incident Response Plan: Prepare a clear, actionable plan for swiftly and effectively responding to security incidents.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly monitor your cloud environment for unusual activity and potential security threats to enable proactive management.
Following these steps can help you create an effective cloud security strategy that protects your data, maintains compliance, and ensures business continuity.
Sources: