According to a recent survey, 80% of companies have experienced at least one cloud security incident in the last year. That is not all; 85% of organizations have cited security as their top cloud challenge, followed by the lack of resources or expertise.
Organizations have also revealed that the aftermath of these cloud security incidents leads to dire consequences. A whopping 69% have reported that the top result is data loss and leakage, followed by data privacy and accidental exposure of credentials.
With 83% of organizations embracing hybrid cloud environments, the need for hybrid cloud security is imminent. This article will explore hybrid cloud security, its components, challenges, and best practices.
What is Hybrid Cloud Security?
Hybrid cloud security protects data, applications, and resources in a hybrid cloud environment. A hybrid cloud combines private cloud infrastructure with public cloud services, allowing businesses to benefit from both environments. Securing a hybrid cloud infrastructure requires a unified approach and strong security posture across environments to address complex cloud deployments. It also aids security teams in managing policies and permissions efficiently.
Let us explore the various components of hybrid cloud security.
Components of Hybrid Cloud Security
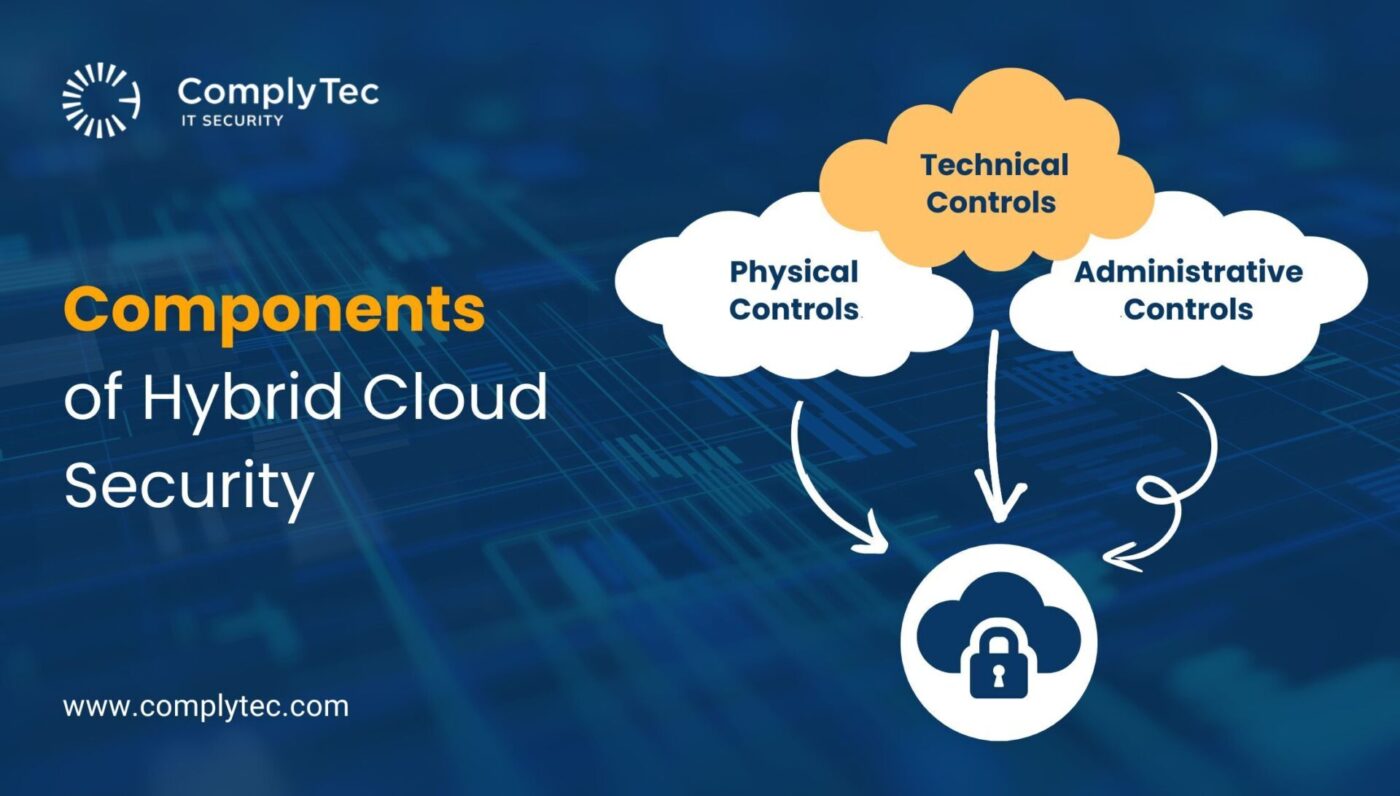
The hybrid cloud security components are based on three categories — Physical, Technical, and Administrative controls. Here is a breakdown of each category:
Physical Controls
Physical controls are critical in hybrid cloud security, protecting the physical infrastructure that supports hybrid cloud environments. Since hybrid cloud environments combine on-premise infrastructure with public and private cloud services, physically securing these environments is very important.
These controls prevent unauthorized physical access to data centers, server rooms, and other critical infrastructure or hardware. Surveillance systems or tools such as
CCTV cameras, key cards, and biometric scanners are considered physical controls. Additionally, an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is considered a physical security control to ensure the infrastructure remains unaffected during a power outage.
Another aspect of physical controls is drawing up Service Level Agreements(SLAs) with public cloud service providers to ensure authorized users can access physical hardware and prevent malicious actors from accessing and misusing it.
Technical Controls
Technical controls focus on protecting data and resources through technology across hybrid cloud environments. A few technical controls include:
Access Controls: Implementing Identity Access Management (IAM) or Cloud Infrastructure Entitlements Management (CIEM) is critical in hybrid cloud protection. These cloud security strategies ensure that only authorized users can access specific resources and data, regardless of whether they reside in the private or public cloud.
Data Encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit is essential to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. This includes encryption protocols that work seamlessly across both cloud environments.
Network Security: Implementing strong network security measures, such as firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection/prevention systems, is crucial. These measures should be adaptable to the dynamic nature of hybrid cloud networks.
Administrative Controls
A crucial aspect of hybrid cloud security is ensuring that all users and stakeholders within an organization know their roles and responsibilities in the event of a security breach. Stakeholders must understand the immediate protocols to provide complete data recovery. Moreover, organizations must create a disaster preparedness plan that security teams can implement to prevent data loss.
With the interconnected nature of hybrid cloud environments, security also becomes the user’s responsibility. Organizations must promote a security-first culture and conduct security training programs for employees and stakeholders to ensure users understand the importance of cloud security and the dire implications of a security breach.
Why is Hybrid Cloud Security Challenging?
While hybrid cloud environments offer numerous benefits for organizations, they come with challenges. Here is why securing hybrid cloud environments can prove to be challenging:
Visibility and Control
Organizations often need help monitoring and securing assets effectively across multiple locations. Maintaining visibility and control over data and workloads in a hybrid cloud is challenging. Public clouds usually offer limited infrastructure visibility, making monitoring and managing security effectively challenging. This lack of visibility can hinder the ability to promptly detect and respond to security incidents.
Complexity and Misconfigurations
Hybrid cloud environments inherently introduce complexity by integrating multiple cloud platforms and on-premises infrastructure. Each platform has its own security settings and management tools, which makes it challenging to maintain a unified security posture. This may lead to common misconfigurations, which often arise from human error or insufficient understanding of the platform’s security features. These misconfigurations can create vulnerabilities attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems.
Management of Access Controls
Managing identities and access controls across hybrid environments is complex. Users need seamless access to resources across different cloud platforms without compromising security. Implementing strong identity and access management (IAM) solutions, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO), is crucial but can be difficult to enforce consistently across all environments.
Adherence to Regulatory Policies
Hybrid cloud deployments complicate compliance and governance efforts due to varying platform requirements. Organizations must demonstrate that they restrict access to protected information and maintain audit trails. Achieving and proving compliance with industry standards and regulations in a hybrid environment requires monitoring, reporting, and auditing tools. The lack of visibility and control over public cloud infrastructure can further aggravate these challenges, making it difficult to ensure that all compliance requirements are met.
Resource Management and Cost Effectiveness
Balancing security and cost efficiency is another challenge in hybrid cloud environments. Organizations must invest in security tools and practices that do not inflate operational costs. Striking the right balance between effective security measures and cost-effective resource management requires meticulous planning and optimization.
Understanding these common challenges can help organizations efficiently protect their hybrid cloud environments. Let us explore the best practices they can implement for adequate hybrid cloud security.
What are the Best Practices for Hybrid Cloud Security?

Securing hybrid cloud environments requires a comprehensive approach that combines various strategies, policies, and tools. Here are some of the best practices organizations can adopt:
Implement Strong Access Controls
Implementing strong access controls is critical for securing hybrid cloud environments. It involves using multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO) to verify user identities. Moreover, organizations must implement role-based access control (RBAC) and the principle of least privilege (PoLP) to ensure users have only limited access to the tasks they need to perform. Organizations must conduct regular audits to understand who has access to their most critical assets and to identify and mitigate potential security risks.
Encrypt Data Everywhere
Data encryption is essential for protecting sensitive information at rest and in transit. Organizations must use strong encryption standards to secure data stored in cloud environments and during transmission across networks. Implementing end-to-end encryption ensures that data remains protected throughout its lifecycle. Additionally, managing encryption keys is crucial to prevent unauthorized access.
Ensure Network Security
Network security measures are vital for protecting hybrid cloud environments as resources are distributed across multiple locations and providers. Organizations can utilize security measures such as network firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), web application firewalls (WAF), intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), cloud workload protection platforms (CWPP), and network segmentation to monitor and control network traffic. This will ensure that traffic is limited to authorized users and applications. Additionally, organizations must regularly update and patch network security tools to protect against the latest threats.
Adopt Consistent Security Policies
Unified security policies across private and public cloud components help maintain a cohesive security posture. These policies should cover data handling, access control, incident response, and compliance requirements. Organizations must regularly review and update policies to adapt to new threats and regulatory changes. This will provide employees with the information required to adhere to these policies, which is critical for maintaining security.
Utilize Monitoring and Threat Detection
Continuous monitoring of cloud environments is crucial for identifying and mitigating security threats in real time. Organizations must have an incident response plan that dictates roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and incident response and escalation procedures. They can also utilize security information and event management (SIEM) systems to collect and analyze data from various sources to detect anomalies. Moreover, organizations can also deploy automated threat detection tools that can enhance their ability to identify and respond to security incidents quickly.
Execute Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Plans
Data backup and disaster recovery plans ensure business continuity during a security breach or data loss. Organizations must regularly back up data and test recovery procedures to ensure they work effectively. Additionally, they can utilize geographically diverse data centers for backups to protect themselves against localized disasters. Organizations can minimize downtime and data loss with a clear and tested disaster recovery plan.
Protect Your Hybrid Cloud Environments with ComplyTec!

ComplyTec is your organization’s trusted partner for cloud security management! We partner with your security team to develop cybersecurity solutions that strengthen protection against threats and vulnerabilities based on your organizational needs.
ComplyTec has provided IT solutions to various North American organizations, including Blue-chip companies and government agencies. We bring vulnerability management, cloud security, and identity security expertise to your organization while enhancing its operational efficiency.
Gain visibility and control over your hybrid cloud environments today with ComplyTec!
Contact Us
FAQs
- How do you protect your hybrid cloud?
To protect your hybrid cloud, your organization must implement strong identity and access management (IAM) with multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC). You must encrypt data in transit and at rest and use powerful network security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Additionally, you must ensure unified security policies across all environments, continuously monitor for threats, and maintain regular compliance audits.
- Which is more secure – private or hybrid cloud?
Neither private nor hybrid cloud environments are inherently secure. The security of private or hybrid cloud environments entirely depends on your organization’s approach to security posture. However, due to its flexibility, hybrid cloud models allow optimized resource use while maintaining strong security protocols.
Sources: